ZEN IRODALOM ZEN LITERATURE
« Zen index
« Home
十牛圖 Shiniu tu [Jūgyūzu]
The Ten Oxherding Pictures
by 普明 Puming [Fumyō], an unknown author
Translated by D. T. Suzuki ( 鈴木 大拙 貞太郎 Suzuki Daisetsu Teitarō, 1870-1966)
"The Ten Oxherding Pictures," translated by D. T. Suzuki, in Manual of Zen Buddhism, Kyoto: Eastern Buddhist Society, 1934. London: Rider & Company, 1950, New York: Grove Press, 1960. pp. 150-171.
VIII
THE TEN OXHERDING PICTURESPreliminary
The author of these "Ten Oxherding Pictures" is said to be a Zen master of the Sung Dynasty known as Kaku-an Shi-en (Kuo-an Shih-yuan) belonging to the Rinzai school. He is also the author of the poems and introductory words attached to the pictures. He was not however the first who attempted to illustrate by means of pictures stages of Zen discipline, for in his general preface to the pictures he refers to another Zen master called Seikyo (Ching-chu), probably a contemporary of his, who made use of the ox to explain his Zen teaching. But in Seikyo's case the gradual development of the Zen life was indicated by a progressive whitening of the animal, ending in the disappearance of the whole being. There were in this only five pictures, instead of ten as by Kaku-an. Kaku-an thought this was somewhat misleading because of an empty circle being made the goal of Zen discipline. Some might take mere emptiness as all important and final. Hence his improvement resulting in the "Ten Oxherding Pictures" as we have them now.
According to a commentator of Kaku-an's Pictures, there is another series of the Oxherding Pictures by a Zen master called jitoku Ki (Tzu-te Hui), who apparently knew of the existence of the Five Pictures by Seikyo, for jitoku's are six in number. The last one, No. 6, goes beyond the stage of absolute emptiness where Seikyo's end: the poem reads:
"Even beyond the ultimate limits there extends a passageway,
Whereby he comes back among the six realms of existence;
Every worldly affair is a Buddhist work,
And wherever he goes he finds his home air;
Like a gem he stands out even in the mud,
Like pure gold he shines even in the furnace;
Along the endless road [of birth and death] he walks sufficient unto himself,
In whatever associations he is found he moves leisurely unattached."Jitoku's ox grows whiter as Seikyo's, and in this particular respect both differ from Kaku-an's conception. In the latter there is no whitening process. In Japan Kaku-an's Ten Pictures gained a wide circulation, and at present all the oxherding books reproduce them. The earliest one belongs I think to the fifteenth century. In China however a different edition seems to have been in vogue, one belonging to the Seikyo and Jitoku series of pictures. The author is not known. The edition containing the preface by Chu-hung, 1585, has ten pictures, each of which is preceded by Pu-ming's poem. As to who this Pu-ming was, Chu-hung himself professes ignorance. In these pictures the ox's colouring changes together with the oxherd's management of him. The quaint original Chinese prints are reproduced below, and also Pu-ming's verses translated into English.
Thus as far as I can identify there are four varieties of the Oxherding Pictures: (1) by Kaku-an, (2) by Seikyo, (3) by Jitoku, and (4) by an unknown author.

1. Undisciplined
With his horns fiercely projected in the air the beast snorts,
Madly running over the mountain paths, farther and farther he goes astray!
A dark cloud is spread across the entrance of the valley,
And who knows how much of the fine fresh herb is trampled under his wild hoofs!

2. Discipline Begun
I am in possession of a straw rope, and I pass it through his nose,
For once he makes a frantic attempt to run away, but he is severely whipped and whipped;
The beast resists the training with all the power there is in a nature wild and ungoverned,
But the rustic oxherd never relaxes his pulling tether and ever-ready whip.

3. In Harness
Gradually getting into harness the beast is now content to be led by the nose,
Crossing the stream, walking along the mountain path, he follows every step of the leader;
The leader holds the rope tightly in his hand never letting it go,
All day long he is on the alert almost unconscious of what fatigue is.

4. Faced Round
After long days of training the result begins to tell and the beast is faced round,
A nature so wild and ungoverned is finally broken, he has become gentler;
But the tender has not yet given him his full confidence,
He still keeps his straw rope with which the ox is now tied to a tree.

5. Tamed
Under the green willow tree and by the ancient mountain stream,
The ox is set at liberty to pursue his own pleasures;
At the eventide when a grey mist descends on the pasture,
The boy wends his homeward way with the animal quietly following.

6. Unimpeded
On the verdant field the beast contentedly lies idling his time away,
No whip is needed now, nor any kind of restraint;
The boy too sits leisurely under the pine tree,
Playing a tune of peace, overflowing with joy.

7. Laissez Faire
The spring stream in the evening sun flows languidly along the willow-lined bank,
In the hazy atmosphere the meadow grass is seen growing thick;
When hungry he grazes, when thirsty he quaffs, as time sweetly slides,
While the boy on the rock dozes for hours not noticing anything that goes on about him.

8. All Forgotten
The beast all in white now is surrounded by the white clouds,
The man is perfectly at his case and care-free, so is his companion;
The white clouds penetrated by the moon-light cast their white shadows below,
The white clouds and the bright moon-light-each following its course of movement.

9. The Solitary Moon
Nowhere is the beast, and the oxherd is master of his time,
He is a solitary cloud wafting lightly along the mountain peaks;
Clapping his hands he sings joyfully in the moon-light,
But remember a last wall is still left barring his homeward walk.
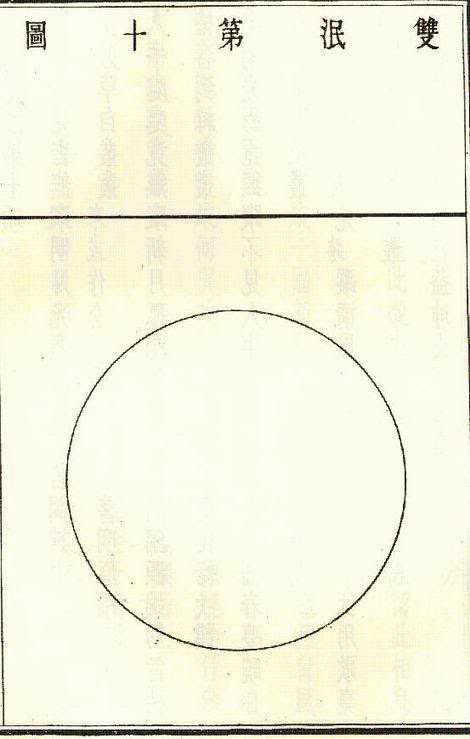
10. Both Vanished
Both the man and the animal have disappeared, no traces are left,
The bright moon-light is empty and shadowless with all the ten-thousand objects in it;
If anyone should ask the meaning of this,
Behold the lilies of the field and its fresh sweet-scented verdure.